Understanding Solar Power Plants
Drafted by: vijaychourey26@gmail.com
In a world seeking sustainable energy solutions, solar power plants have emerged as a beacon of hope. The remarkable ability to harness the sun's abundant energy presents a vital step towards reducing our carbon footprint and transitioning towards cleaner energy sources. In this article, we'll delve into the intricate workings of solar power plants, exploring their components, benefits, and the role they play in shaping our energy future.
Introduction to Solar Power Plants
Solar power plants are revolutionary energy facilities that convert sunlight directly into electricity. Unlike fossil fuels, which contribute to pollution and climate change, solar power is a clean, abundant, and renewable energy source.
How Solar Power Plants Work
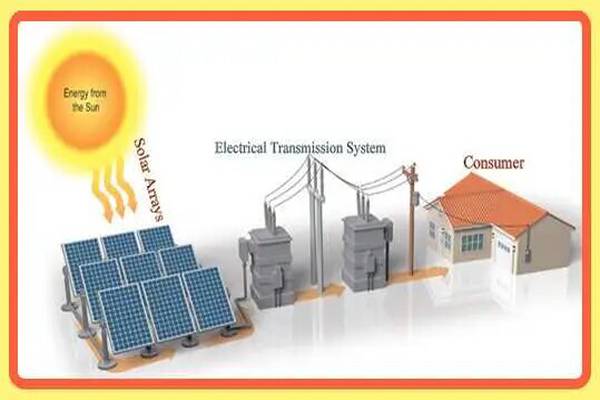
At the heart of solar power plants are photovoltaic (PV) cells, which contain semiconductor materials that generate electricity when exposed to sunlight. When sunlight hits these cells, electrons are released, creating an electric current. This current is then captured and converted into usable electricity.
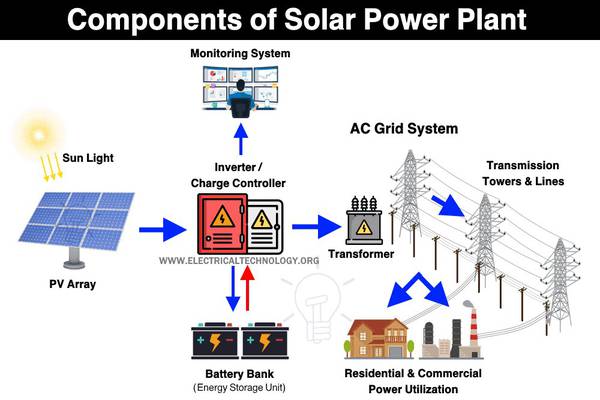
Components Of A Solar Power Plant
Photovoltaic Panels
PV panels, often referred to as solar panels, are the workhorses of solar power plants. These panels consist of multiple interconnected PV cells that work together to generate electricity.
Inverters: Converting DC to AC
The direct current (DC) electricity produced by PV cells needs to be converted into alternating current (AC) for use in homes and businesses. Inverters perform this crucial function.
Energy Storage Systems
Energy storage systems, such as batteries, store excess energy produced during sunny periods. This stored energy can be utilized during cloudy days or at night when sunlight is unavailable.
Tracking Systems: Maximizing Efficiency
Solar panels are equipped with tracking systems that allow them to follow the sun's path across the sky. This dynamic orientation maximizes energy absorption and efficiency throughout the day.
Types Of Solar Power Plants
Solar Photovoltaic Plants
PV plants are the most common type, using arrays of PV panels to directly convert sunlight into electricity.
Concentrated Solar Power Plants
These plants use mirrors or lenses to concentrate sunlight onto a small area, generating intense heat that drives turbines to produce electricity.
Hybrid Solar Power Plants
Hybrid plants combine solar power with other energy sources, such as wind or natural gas, for consistent energy generation.
Advantages Of Solar Power Plants
Clean and Renewable Energy Source
Solar power is inexhaustible, making it an essential tool in reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Reduction in Greenhouse Gas Emissions
By generating electricity without emissions, solar power plants contribute significantly to reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Low Operating Costs and Maintenance
Once installed, solar power plants have minimal operating and maintenance expenses compared to traditional power plants.
Job Creation and Economic Benefits
The solar industry has created numerous job opportunities and economic growth, benefiting local communities.
Solar Power In Agriculture: An Overview
Irrigation Systems Powered by Solar Energy
Solar-powered irrigation systems have transformed farming practices in areas with limited access to conventional power sources. These systems use solar energy to pump water from wells or other water sources, ensuring a consistent and efficient water supply for crops.
Solar-Powered Greenhouses
Solar-powered greenhouses combine modern technology with traditional farming methods. These structures use transparent solar panels to capture sunlight, creating a controlled environment for crops. They extend the growing season, optimize temperature and humidity, and reduce energy costs.
Electric Fencing and Security
Solar-powered electric fencing is a sustainable solution to protect crops from wildlife and intruders. The energy harnessed during the day powers the fencing system, providing a reliable and eco-friendly security measure.
Solar-Powered Crop Drying
Solar dryers are an effective way to preserve harvested crops. By using solar energy to heat and circulate air, these dryers reduce moisture content in crops, preventing spoilage and enhancing their shelf life.
Remote Monitoring and Surveillance
Solar-powered surveillance systems help farmers keep an eye on their fields and livestock remotely. These systems use solar energy to power cameras and sensors, enhancing security and facilitating real-time monitoring.
Solar-Powered Equipment
Farm equipment such as water pumps, tractors, and tools can be powered by solar energy. This reduces operating costs and reliance on fossil fuels, contributing to a more sustainable and economical farming operation.
Microgrid Solutions for Rural Farming
Solar-powered microgrids provide energy access to remote and off-grid farming communities. These microgrids combine solar energy with battery storage, ensuring a continuous power supply for essential activities.
Government Incentives and Support
Many governments offer incentives and subsidies to promote solar power adoption in agriculture. These incentives can significantly reduce the initial investment and encourage farmers to embrace renewable energy solutions.
Challenges In Solar Power Generation
Intermittency and Energy Storage
Solar power generation depends on sunlight availability, necessitating effective energy storage solutions.
Initial Installation Costs
While operating costs are low, the initial investment in solar power plants can be substantial.
Land Requirement and Environmental Impact
Large solar installations require considerable land space, potentially impacting ecosystems and communities.
The Future Of Solar Power Plants
Technological Innovations
Ongoing advancements in PV technology continue to improve efficiency and decrease costs.
Integration with Smart Grids
Solar power plants are becoming integral parts of smart grids, enhancing energy distribution and consumption.
Solar Power in Urban Planning
Solar integration in urban architecture is reshaping city landscapes and reducing the strain on traditional power grids.