Hydroponics: Revolutionizing Agriculture Through Soilless Cultivation
Drafted by: vijaychourey26@gmail.com
In recent years, hydroponics has emerged as a groundbreaking method of cultivating plants without traditional soil-based systems. This innovative technique involves growing plants in nutrient-rich water solutions, providing them with optimal conditions for growth. With its potential to revolutionize agriculture, hydroponics offers a sustainable and efficient way to produce crops. In this article, we'll delve into the world of hydroponics, exploring its various methods, benefits, and the future it holds.
Understanding Hydroponics
Hydroponics at a Glance
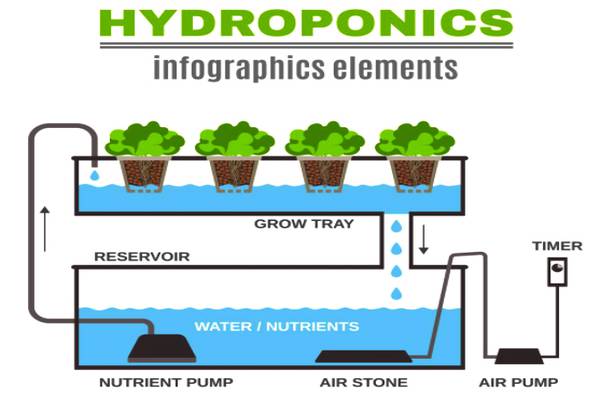
Hydroponics is a cultivation method where plants are grown in a controlled environment without soil. Instead, they receive essential nutrients through water, ensuring maximum absorption and minimal wastage. This method eliminates the need for traditional farming practices, such as plowing, weeding, and tilling, leading to increased efficiency and reduced environmental impact.
Historical Roots of Hydroponics
The concept of hydroponics dates back to ancient civilizations like the Babylonians and Aztecs, who practiced plant cultivation in water-enriched solutions. However, the modern hydroponic systems we see today have evolved significantly, integrating technology and scientific knowledge to enhance plant growth and yields.
Methods Of Hydroponics
1. Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)
NFT involves a continuous flow of nutrient solution over plant roots, providing a thin film of water that supplies essential nutrients. This method is efficient and conserves water, making it ideal for smaller spaces.
2. Deep Water Culture (DWC)
In DWC, plant roots are submerged in a nutrient solution with an oxygenating mechanism. This method offers excellent aeration and is commonly used for cultivating lettuce, herbs, and other leafy greens.
3. Ebb and Flow System
Also known as the flood and drain system, this method periodically floods the root zone with the nutrient solution and then drains it. It's versatile and suitable for a wide range of plants.
Benefits Of Hydroponics
1. Water Conservation
Hydroponics uses up to 90% less water compared to traditional soil-based agriculture. The recirculation of nutrient solutions reduces wastage, making it an eco-friendly choice.
2. Faster Growth Rates
Plants in hydroponic systems grow up to 25% faster due to the direct availability of nutrients. This results in higher yields and quicker harvest cycles.
3. Space Efficiency
Hydroponics is perfect for urban farming or areas with limited space. Vertical systems and controlled environments maximize space utilization.
4. Pest and Disease Control
Since hydroponic setups are enclosed, the risk of pests and diseases is minimized. This reduces the need for chemical pesticides, promoting healthier produce.
Types Of Hydroponic Systems
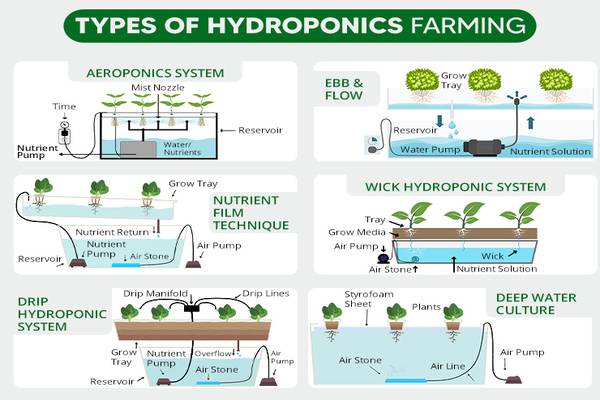
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)
The NFT system involves a continuous flow of nutrient solution over plant roots, creating a thin nutrient film. This method is known for its efficiency in water and nutrient use, making it suitable for small to medium-sized plants.
Deep Water Culture (DWC)
In DWC, plant roots are submerged in a nutrient solution, providing oxygen through air pumps. This system's simplicity and cost-effectiveness have made it a popular choice among beginners.
Drip System
Drip systems deliver nutrient solutions directly to plant bases through a network of tubes and emitters. This precise method offers excellent control over nutrient delivery.
Wick System
The wick system is one of the simplest hydroponic setups. It employs a wick to passively draw nutrient solution from a reservoir to the plant roots. This method is best suited for smaller plants and herbs.
Ebb and Flow System
Also known as the flood and drain system, this method periodically floods the plant roots with nutrient solution and then allows it to drain. It provides a balance between moisture and oxygen levels.
Aeroponics
Aeroponics suspends plants in the air and mists their roots with a nutrient solution. This high-oxygen, high-moisture environment promotes rapid growth and is commonly used for delicate plants.
Challenges In Hydroponics
Nutrient Imbalance
Maintaining the correct nutrient balance can be challenging, as excessive or deficient nutrients can harm plant growth.
Disease Susceptibility
With plants in close proximity, hydroponic systems are susceptible to rapid disease spread. Controlling diseases requires vigilance and proper sterilization.
Technical Complexity
Certain hydroponic systems demand technical expertise in setup and maintenance, potentially deterring newcomers.
Initial Investment
The initial costs of hydroponic systems, including equipment and setup, can be higher compared to traditional farming.
Monitoring and Maintenance
Constant monitoring of nutrient levels, pH, and water flow is essential. Neglecting maintenance can lead to crop failure.
Mitigating Challenges
Nutrient Management Strategies
Regularly testing and adjusting nutrient solutions can help maintain optimal nutrient levels for healthy plant growth.
Implementing Proper Sterilization
Sanitizing equipment, growing medium, and water sources can significantly reduce disease risks.
Education and Training
Proper training and resources can empower growers to confidently manage hydroponic systems.
Cost-effective Approaches
Exploring DIY options and gradually expanding the setup can ease the financial burden.
Automation and Monitoring Tools
Using technology for automated nutrient delivery and remote monitoring can simplify maintenance.
Future Of Hydroponics
Technological Innovations: Sensors, data analytics, and smart controllers enhance efficiency.
Integration with Urban Farming: Hydroponics plays a crucial role in sustainable city farming.
Sustainability and Food Security: Hydroponics contributes to year-round crop production and reduces water wastage.