Harvester In Agriculture
Drafted by: vijaychourey26@gmail.com
In the ever-evolving landscape of agriculture, technological advancements continue to reshape traditional farming practices. One such innovation that has transformed the way crops are harvested is the modern harvester. With the ability to efficiently and effectively gather crops, harvester machines have become indispensable tools for farmers around the world. In this article, we'll delve into the intricacies of harvesters in agriculture, exploring their types, benefits, and impact on the farming industry.
Harvesting crops has long been a labor-intensive and time-consuming process in agriculture. However, with the advent of harvesters, this essential task has been revolutionized. Harvesters are specialized machines designed to automate the process of collecting ripe crops from fields, making the entire operation more efficient and cost-effective.
Types Of Harvesters
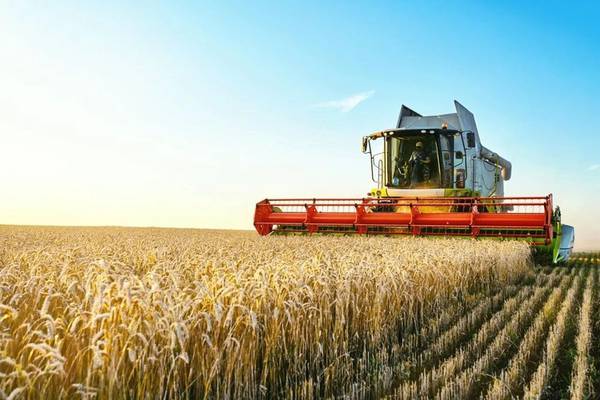
Combine Harvesters
Combine harvesters, often referred to simply as "combines," are versatile machines that handle multiple tasks in a single pass. They can cut, thresh, and clean the harvested crop, making them ideal for large-scale grain production. Combines are equipped with various headers that can be swapped out to accommodate different crops.
Forage Harvesters
Forage harvesters, commonly used in livestock farming, are designed to gather and chop crops such as corn, grass, and other silage materials. These machines are crucial for producing nutritious feed for animals and are known for their ability to efficiently process and store forage.
Cotton Pickers
Cotton pickers are specialized harvesters designed to mechanize the process of picking cotton bolls from the plants. They greatly reduce the labor-intensive nature of cotton harvesting and contribute to increased productivity in the cotton industry.
Sugar Beet Harvesters
Sugar beet harvesters are tailored to the needs of root crop harvesting. They carefully extract sugar beets from the soil, minimizing damage and ensuring that the valuable crop is preserved during the harvesting process.
Advantages Of Using Harvesters
Increased Efficiency
Harvesters dramatically improve harvesting efficiency, allowing farmers to gather crops at a faster rate compared to manual methods. This increased speed is particularly beneficial during peak harvesting seasons.
Labor Savings
The automation provided by harvesters reduces the need for manual labor in the fields. This not only addresses labor shortages but also frees up human resources for other essential farming tasks.
Reduced Crop Loss
Harvesters are designed to handle crops delicately, minimizing bruising and damage. This translates to reduced crop loss during the harvesting process, resulting in higher yields.
How Harvesters Work
Threshing
Threshing involves separating the edible part of the crop from the non-edible parts, such as the husks or stalks. This is achieved through mechanical beating or rubbing.
Separation
After threshing, the harvested material is separated based on density. Heavier grains or seeds fall while lighter materials are blown away, ensuring only the desired crop is collected.
Cleaning
The final step involves cleaning the harvested crop to remove any remaining impurities, ensuring the quality of the yield.
Impact On Crop Quality
Preservation of Crop Integrity
Harvesters handle crops with precision, minimizing physical damage and preserving the overall quality of the harvested produce.
Minimized Contamination
The closed-system design of harvesters reduces the chances of contamination during harvesting, contributing to cleaner and safer crops.
Environmental Considerations
Reduced Chemical Usage
Harvesters' efficient gathering methods help reduce the need for chemical treatments, promoting more sustainable farming practices.
Soil Health and Conservation
By minimizing soil compaction and disturbance, harvesters contribute to improved soil health and long-term soil conservation.
Adoption And Future Trends
Precision Agriculture Integration
Harvesters are increasingly integrated with precision agriculture technologies, allowing for data-driven decisions and optimized harvesting practices.
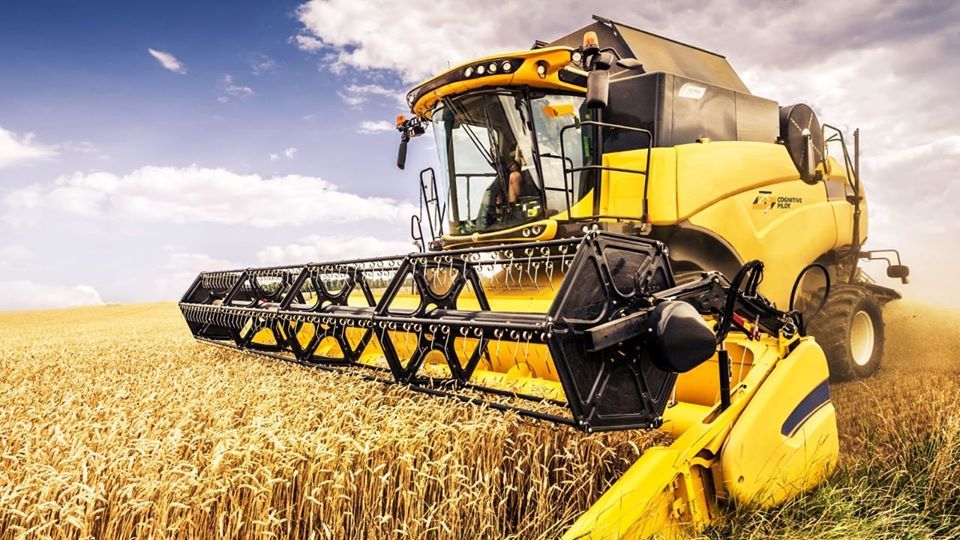
Autonomous Harvesting
The future holds the promise of fully autonomous harvesters, guided by AI and GPS technologies, further enhancing efficiency and reducing human intervention.
Challenges And Limitations
Initial Investment
Acquiring harvesters can be a significant upfront investment, particularly for small-scale farmers.
Adaptation to Crop Varieties
Harvesters' efficiency may vary across different crop types and varieties, requiring adaptations and adjustments.