Fertigation System: Nutrient Delivery
Drafted by: vijaychourey26@gmail.com
In the realm of modern agriculture, the quest for efficiency and sustainability is an ongoing endeavor. One remarkable innovation that has gained significant traction is the fertigation system. This revolutionary technique merges fertilization and irrigation, allowing farmers to provide precise and controlled nutrient delivery to their crops. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of the fertigation system, its benefits, implementation, and its role in shaping the future of agriculture.
Fertigation, a portmanteau of "fertilization" and "irrigation," is a modern agricultural practice that has transformed the way nutrients are supplied to crops. This ingenious system allows farmers to administer fertilizers through irrigation systems, resulting in efficient and targeted nutrient uptake by plants. By seamlessly integrating these two vital processes, fertigation holds the promise of maximizing crop yield while minimizing resource wastage.
Understanding Nutrient Management In Agriculture
The Importance of Nutrients for Plant Growth
Plants rely on essential nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, for their development and overall health. These nutrients play a pivotal role in various physiological processes, including photosynthesis and root development. In traditional farming methods, nutrients are often applied to the soil separately from irrigation, leading to uneven distribution and nutrient loss.
Challenges in Traditional Nutrient Delivery
Traditional methods of nutrient application face challenges in delivering nutrients precisely to plant roots. Uneven distribution, nutrient leaching, and excessive resource consumption have been persistent issues. Fertigation emerges as a solution to these problems by directly infusing nutrients into the irrigation water, ensuring that plants receive a consistent and balanced supply.
How Fertigation Works: The Science Behind It
Types of Fertilizers Used in Fertigation
Fertigation accommodates various types of fertilizers, including water-soluble fertilizers and liquid fertilizers. These are easily dissolved in water and can be seamlessly integrated into irrigation systems.
Components of a Fertigation System
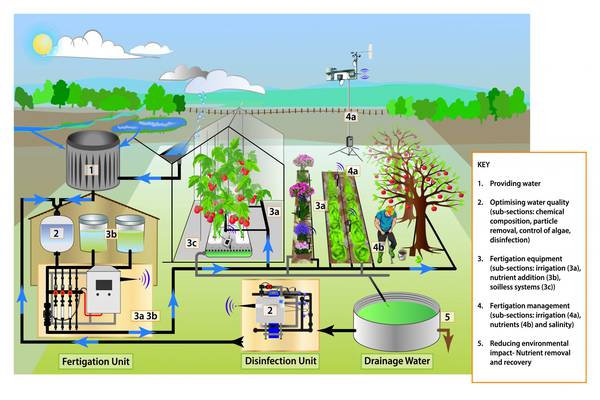
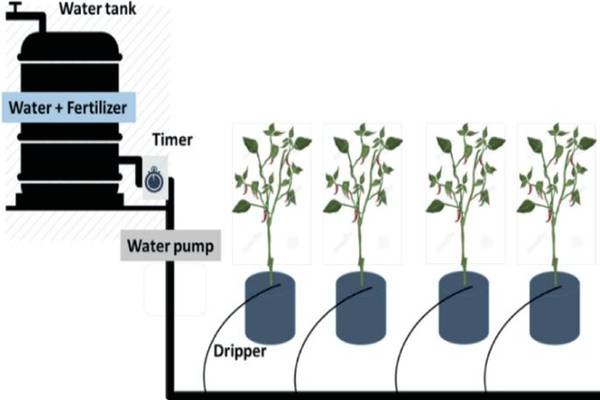
A typical fertigation system comprises several key components, including a fertilizer injector, a water supply network, a controller, and a filtration system. The fertilizer injector accurately mixes the fertilizer solution with the irrigation water, while the controller regulates the injection rate and timing.
Advantages Of Fertigation In Agriculture
Enhanced Nutrient Absorption
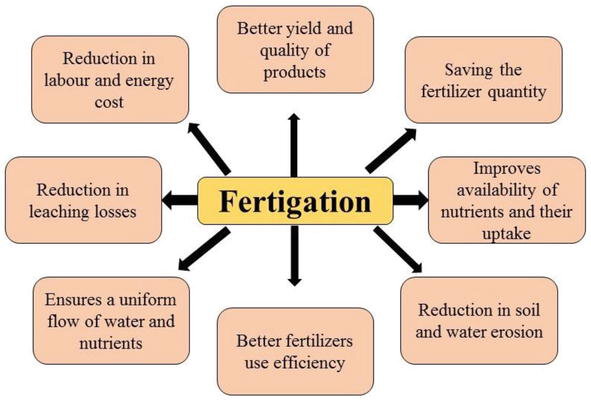
Fertigation optimizes nutrient absorption by delivering them directly to the root zone. This targeted approach promotes efficient utilization, minimizing nutrient wastage.
Water Conservation and Reduced Leaching
Traditional fertilization methods often lead to nutrient leaching and water wastage. Fertigation addresses this concern by delivering nutrients in controlled doses, reducing the risk of over-fertilization and its environmental impact.
Precision and Customization
Fertigation enables farmers to tailor nutrient delivery according to specific crop requirements, growth stages, and soil conditions. This customization fosters healthier plants and higher yields.
Implementing Fertigation On Different Crops
Fruit Orchards
Fertigation has shown remarkable results in fruit orchards, where precise nutrient delivery significantly improves fruit quality and size.
Vegetable Cultivation
Vegetable growers benefit from fertigation's ability to deliver nutrients evenly, resulting in uniform crop growth and consistent produce quality.
Field Crops
Fertigation can be adapted to various field crops, enhancing nutrient distribution across large agricultural landscapes.
Steps To Set Up An Efficient Fertigation System
Water Source and Filtration
A reliable water source and effective filtration system are crucial for preventing clogs and maintaining the integrity of the fertigation equipment.
Fertilizer Injection Equipment
Choosing the appropriate fertilizer injector based on the type of fertilizers used and the irrigation system in place ensures accurate mixing and delivery.
Irrigation System Compatibility
Integrating fertigation with the existing irrigation system demands compatibility and proper synchronization to achieve optimal results.
Overcoming Challenges And Best Practices
Monitoring and Maintenance
Regular monitoring of the fertigation system, along with prompt maintenance and repairs, ensures consistent nutrient delivery and system efficiency.
Preventing Clogging and Blockages
Proper filtration, using clean water sources, and employing compatible fertilizers help prevent clogs and blockages that can disrupt nutrient flow.
Fertigation And Sustainability: A Greener Approach
Reducing Environmental Impact
Fertigation's controlled nutrient delivery reduces the risk of nutrient runoff and groundwater contamination, contributing to a more sustainable agricultural ecosystem.
Mitigating Soil Degradation
By delivering nutrients directly to the root zone, fertigation minimizes soil compaction and degradation associated with traditional fertilization methods.
Future Prospects Of Fertigation
Technological Advancements
Continued technological innovations are expected to refine fertigation systems, making them more efficient, user-friendly, and adaptable.
Integration with Smart Farming
Fertigation is likely to be integrated into smart farming practices, leveraging data and automation for even more precise nutrient delivery.