Explore Livestock Feed
Drafted by: vijaychourey26@gmail.com
Livestock farming is a crucial aspect of agriculture, providing a steady supply of meat, dairy products, and other essentials to meet the demands of our growing population. A significant factor in ensuring the health and productivity of livestock is their feed. In this article, we'll delve into the world of livestock feed, understanding its importance, types, nutritional considerations, and sustainable practices.
Introduction
Livestock feed plays a critical role in ensuring the overall health, growth, and productivity of animals raised for meat, milk, and other products. The quality and composition of the feed have a direct impact on the nutritional value of the end products and the well-being of the animals.
Importance of Quality Feed:
Quality feed provides the essential nutrients that animals need to thrive. It affects their growth rate, reproductive performance, immune system, and overall vitality. Poor-quality feed can lead to deficiencies, diseases, and reduced productivity, impacting both the animals and the farmers' income.
Impact on Product Quality:
The feed animals consume directly impacts the quality, flavor, and nutritional value of the end products, such as meat and dairy.
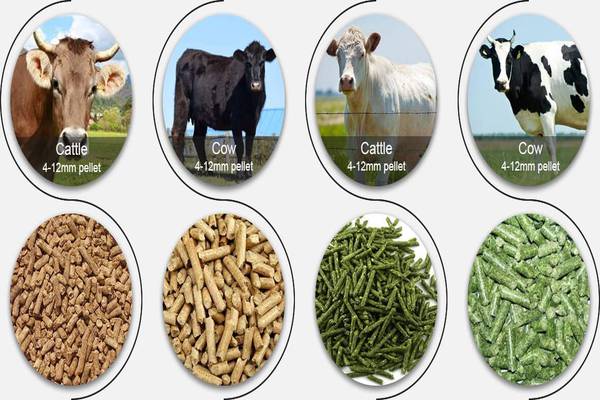
Types Of Livestock Feed
Hay and Forage
Hay and forage, such as grass and alfalfa, are staple feeds for ruminant animals like cattle and sheep. They provide fiber, which aids in digestion and promotes gut health.
Grains and Concentrates
Grains like corn, barley, and oats, along with concentrates, are energy-rich feeds suitable for various livestock. They are especially important for animals with high energy needs, such as poultry and pigs.
Protein Supplements
Protein supplements, including soybean meal and fishmeal, are vital for muscle development and milk production in dairy cattle and other animals.
Mineral and Vitamin Supplements
These supplements ensure that animals receive necessary minerals and vitamins for bone development, metabolic processes, and overall well-being.
Nutritional Requirements
Proteins and Amino Acids
Proteins are essential for growth and tissue repair. Amino acids, the building blocks of proteins, must be balanced in the feed to support optimal health.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates provide energy for daily activities and bodily functions. They are particularly important for lactating animals and those engaged in physical labor.
Fats
Dietary fats contribute to energy storage, insulation, and the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins.
Vitamins and Minerals
Vitamins and minerals play vital roles in various physiological processes, including immune response, bone development, and reproduction.
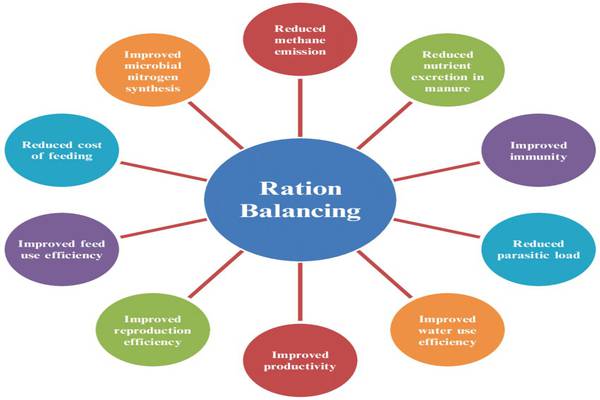
Balancing Feed Rations
Creating balanced feed rations involves combining different types of feed to meet the nutritional requirements of specific animals. This ensures that they receive the right proportions of proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, and minerals.
Innovations In Livestock Feed
Precision Nutrition
Modern technology allows farmers to formulate precise feed rations based on an animal's age, weight, and nutritional needs.
Alternative Protein Sources
Researchers are exploring insect-based and plant-based proteins as sustainable alternatives to traditional protein sources.
Sustainable Feed Production
Efforts are being made to reduce the environmental impact of feed production, including optimizing resource use and minimizing waste.
Feed Management Practices
Feeding Frequency and Quantity
Establishing consistent feeding schedules and providing appropriate quantities of feed contribute to optimal growth and health.
Water Availability
Access to clean and abundant water is crucial for digestion, nutrient absorption, and temperature regulation.
Preventing Feed Contamination
Proper storage and handling practices are essential to prevent contamination by mold, toxins, and pathogens.
Addressing Livestock-Specific Needs
Dairy Cattle
Dairy cattle require specialized feed for high milk production, including nutrients like calcium and phosphorus.
Poultry
Poultry feed formulations vary based on whether the birds are raised for meat or eggs, with different nutrient requirements for each.
Swine
Swine feed focuses on rapid growth and lean meat production, with careful attention to protein and energy content.
Sheep and Goats
These animals often thrive on forage-based diets, supplemented with minerals and proteins to support growth and wool production.
Sustainable Feed Practices & Future Of Livestock Feed
Local Sourcing
Sourcing feed ingredients locally reduces transportation emissions and supports local economies.
Reducing Food Waste
Minimizing food waste at farms and processing facilities contributes to efficient resource utilization.
Alternative Ingredients
Incorporating byproducts and alternative ingredients into feed formulations can make the livestock industry more sustainable.
The Future of Livestock Feed:
Technological Advancements
Advances in data analytics and biotechnology will continue to shape the way livestock nutrition is understood and managed.
Circular Agriculture
The concept of circular agriculture involves using waste and byproducts to create feed, closing the loop in resource utilization.