Explore Biodynamic Farming: A Holistic Approach To Sustainable Agriculture
Drafted by: vijaychourey26@gmail.com
In recent years, the global agricultural landscape has been undergoing a significant transformation, with a growing emphasis on sustainable and environmentally friendly practices. One such approach gaining traction is biodynamic farming, a holistic method that goes beyond organic farming to create a truly interconnected and balanced agricultural ecosystem. In this article, we will delve into the principles, practices, and benefits of biodynamic farming, uncovering how it fosters harmony between nature, plants, animals, and humans.
Introduction To Biodynamic Farming
Biodynamic farming is an agricultural approach that recognizes the intricate relationships between soil, plants, animals, and the cosmos. Rooted in the principles of Austrian philosopher Rudolf Steiner, this method seeks to create a self-sustaining and balanced ecosystem within the farm. Unlike conventional farming, which often relies on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, biodynamic farming utilizes natural processes to nurture the land and its inhabitants.
The Foundations Of Biodynamic Farming
Understanding the Biodynamic Approach
At its core, biodynamic farming is an agricultural philosophy that views the farm as a self-sustaining entity. This method is built upon the principles laid out by Rudolf Steiner in the 1920s, which emphasize the interplay of cosmic forces, lunar cycles, and natural rhythms within the farming system. Biodynamic farmers see their farms as living organisms, with the goal of achieving a harmonious relationship between the soil, plants, animals, and humans.
Anthroposophy and Agriculture
At the heart of biodynamic farming lies anthroposophy, a philosophy developed by Rudolf Steiner that emphasizes the spiritual and mystical aspects of human existence. Steiner believed that by understanding and harmonizing with cosmic forces, farmers could optimize the health and vitality of their farms. This holistic approach extends to both the physical and metaphysical realms, encouraging farmers to view their land as a living organism.
Cosmic Rhythms and Planting Calendar
Biodynamic farmers follow a planting calendar that considers the movements of the moon and planets. It is believed that these cosmic rhythms influence the growth and development of plants. Certain days are considered optimal for planting, cultivating, and harvesting various crops. By aligning agricultural activities with celestial events, biodynamic farmers aim to enhance plant vitality and overall farm productivity.
Stay tuned for the next sections where we'll delve into the key principles of biodynamic farming and explore its unique practices.
Key Principles Of Biodynamic Farming
Diversity and Polyculture
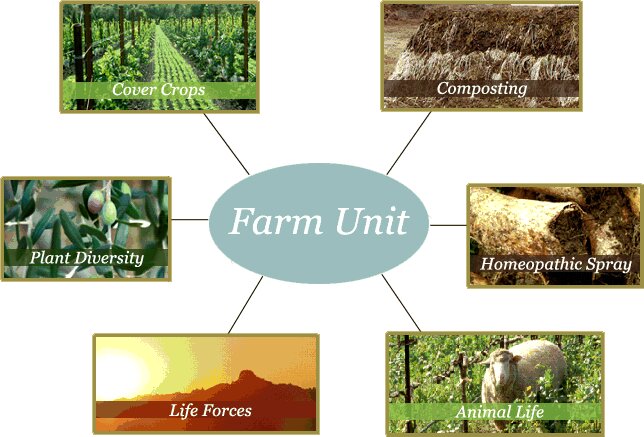
In biodynamic farming, diversity is not only celebrated but actively promoted. Farmers cultivate a variety of crops, often intermingling them in a practice known as polyculture. This approach mimics natural ecosystems and reduces the risk of crop failure due to pests or diseases. By growing multiple crops together, the farm becomes more resilient and less dependent on external inputs.
Composting and Soil Enrichment
Soil health is a cornerstone of biodynamic farming. Instead of relying on synthetic fertilizers, biodynamic farmers prioritize composting and natural soil enrichment techniques. Compost, often enriched with biodynamic preparations, nourishes the soil and enhances its structure. Healthy soil, in turn, promotes robust plant growth and nutrient-rich produce.
Integration of Livestock
Biodynamic farms often integrate livestock into their operations. Animals play a crucial role in nutrient cycling and soil fertility. Their manure contributes to composting efforts, while their presence encourages a balanced ecosystem. Animals and plants work in harmony, creating a closed-loop system that minimizes waste and maximizes resource utilization.
The Practices Of Biodynamic Farming
Biodiversity and Self-Sufficiency
One of the cornerstones of biodynamic farming is biodiversity. Farms are designed to be self-sufficient ecosystems, incorporating a variety of plants and animals that complement and support one another. This diversity helps control pests naturally, reduces the reliance on external inputs, and promotes a balanced and resilient ecosystem.
Composting and Preparation
Biodynamic farming places a strong emphasis on composting and utilizing specific preparations that enhance soil health and plant vitality. These preparations, often made from herbs, minerals, and animal manures, are carefully combined and applied to the soil to stimulate microbial activity, improve nutrient availability, and bolster plant resistance to diseases.
Integration of Animals
Unlike conventional farming, where animals are often raised separately from crops, biodynamic farms integrate animals directly into the system. Animals contribute to soil fertility through their manure, aid in pest control, and play a role in balancing the ecosystem dynamics.
The Benefits Of Biodynamic Farming
Enhanced Nutritional Value
Proponents of biodynamic farming assert that the holistic approach leads to produce with higher nutritional value and improved taste. By focusing on soil health and the overall well-being of the farm, biodynamic practices result in crops that are more nutrient-dense and flavorful.
Environmental Sustainability
Biodynamic farming prioritizes environmental sustainability by reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers and pesticides. The emphasis on self-sufficiency, composting, and natural pest management minimizes the farm's ecological footprint, making it a more sustainable and regenerative practice.
Enhancing Biodiversity and Ecosystem Health:
Role of Cover Crops
Cover crops are an integral part of biodynamic farming systems. These crops are grown primarily to protect and improve the soil rather than for direct consumption. They prevent erosion, suppress weeds, and add organic matter to the soil as they decompose. The inclusion of cover crops in crop rotation strategies contributes to soil fertility and structure.
Companion Planting Techniques
Biodynamic farmers employ companion planting to encourage symbiotic relationships between different plant species. Certain plants naturally repel pests or provide nutrients that benefit neighboring plants. By strategically interplanting compatible species, farmers can reduce the need for chemical interventions and promote a healthier, more balanced ecosystem.
Continue reading to discover the differences between biodynamic and organic farming approaches.
Biodynamic Vs. Organic Farming
Focus on Spiritual and Cosmic Aspects
One of the distinctive features of biodynamic farming is its emphasis on spiritual and cosmic influences. Practitioners believe that by considering celestial rhythms and metaphysical energies, they can create a farm that resonates with the universe. Organic farming, while ecologically conscious, does not incorporate these esoteric elements.
Holistic Approach to Sustainability
Biodynamic farming's holistic approach sets it apart from traditional organic farming. It views the farm as a self-sustaining organism interconnected with the surrounding environment. This perspective goes beyond simply avoiding synthetic inputs; it aims to foster a regenerative and harmonious relationship between the farm and nature.
Stay tuned for insights into biodynamic certification and successful case studies of biodynamic farms.
Biodynamic Certification And Practices Worldwide
Biodynamic farming has gained recognition worldwide, with various organizations offering certification to farms that adhere to its principles. One such organization is Demeter International, which provides biodynamic certification based on strict criteria. Certified farms demonstrate their commitment to ecological balance, animal welfare, and holistic farming practices.
Case Studies: Successful Biodynamic Farms
Demeter International Certified Farms
Apricot Valley: This biodynamic farm in California, USA, produces a diverse range of fruits, vegetables, and herbs. By following biodynamic practices, Apricot Valley has experienced improved soil fertility and increased crop resilience.
Harmony Fields: Located in Australia, Harmony Fields is a certified biodynamic farm known for its holistic approach to wine grape cultivation. The farm's practices reflect a harmonious blend of ecological principles and cosmic awareness.
Challenges and Criticisms of Biodynamic Farming
While biodynamic farming offers numerous benefits, it also faces challenges and criticisms.
The Future of Biodynamic Agriculture:
As the demand for sustainable and environmentally conscious farming practices grows, biodynamic agriculture is poised to play an essential role. Its focus on regenerative principles, holistic ecosystem management, and cosmic alignment resonates with a world seeking more than just food production—it seeks agricultural systems that support the health of the planet.