Explore Agricultural Policy: Navigating The Path To Sustainable Farming
Drafted by: vijaychourey26@gmail.com
Agricultural policy plays a pivotal role in shaping the landscape of farming practices, environmental sustainability, and rural economies. In this article, we'll delve into the intricate world of agricultural policy, its significance, key components, challenges, and its impact on farmers, consumers, and the environment. By the end of this exploration, you'll have a clearer understanding of how agricultural policy sets the stage for the future of food production. Agricultural policy serves as the compass that guides the agricultural sector towards sustainable practices while ensuring food security and economic growth. This article takes a comprehensive look at the multifaceted aspects of agricultural policy, shedding light on its evolution, objectives, environmental implications, challenges, and the global context.
The Evolution Of Agricultural Policy
From its origins in the early 20th century, agricultural policy has transformed significantly. Initially focusing on production incentives to address food scarcity, it now encompasses a broader spectrum of concerns including environmental impact, trade relationships, and equitable resource distribution.
Objectives of Agricultural Policy:
The core objectives of agricultural policy revolve around ensuring a stable food supply, enhancing rural livelihoods, and fostering economic development. These objectives are achieved through a combination of regulatory measures, financial support, and market interventions.
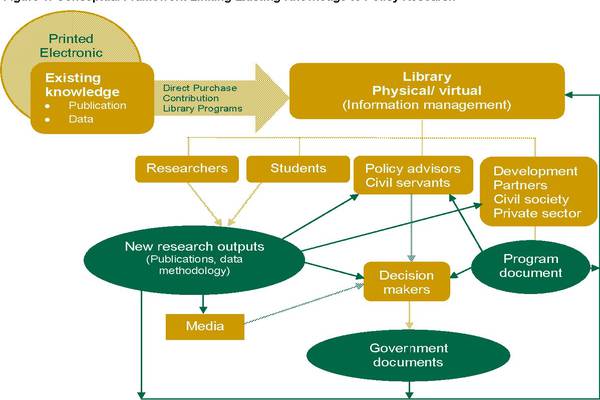
The Role Of Research And Data
Informed decision-making relies on accurate data and ongoing research.
Informed Decision Making
Policies rooted in evidence-based research yield more favorable outcomes for both farmers and the environment.
Adapting Policies to Changing Conditions
Flexible policies that can adapt to evolving challenges and technological advancements are crucial for long-term sustainability.
Government Interventions In Agriculture
Governments play a central role in shaping agricultural policy through various interventions. Subsidies provide essential financial support to farmers, price controls maintain market stability, and trade policies influence international relations.
Subsidies and Financial Support
Financial assistance programs empower farmers to invest in modern technologies, infrastructure, and training, thereby boosting productivity and income stability.
Price Controls and Market Regulation
Price stabilization mechanisms prevent extreme fluctuations, guaranteeing fair returns to farmers and reasonable prices for consumers.
Trade Policies and Import/Export
Regulating import and export activities ensures domestic market protection while fostering global trade relationships.
Environmental Considerations
Modern agricultural policy places increasing emphasis on environmental sustainability, recognizing the pivotal role of farming in ecosystem health.
Sustainable Farming Incentives
Policy frameworks encourage sustainable practices such as crop rotation, agroforestry, and reduced chemical usage, promoting long-term soil fertility and biodiversity.
Conservation Practices and Land Use
Agricultural policy advocates for responsible land management to prevent deforestation, soil erosion, and habitat destruction.
Challenges In Agricultural Policy Implementation
Balancing Economic and Environmental Concerns
Striking a balance between economic growth and environmental protection demands innovative approaches that minimize negative externalities.
Small vs. Large-Scale Farming
Policies must cater to the needs of both small-scale subsistence farmers and large-scale commercial operations to ensure inclusivity.
Global Trade Dynamics
Navigating global trade intricacies requires policies that shield domestic farmers from unfair competition while upholding international agreements.
Innovations In Agricultural Policy
Technology Integration in Farming
Smart farming technologies, such as precision agriculture and IoT devices, enable efficient resource utilization and data-driven decision-making.
Promotion of Organic Farming
Agricultural policy supports the organic farming movement, responding to the demand for chemical-free, environmentally friendly produce.
Impact Of Agricultural Policy
Impact on Farmers
Agricultural policy directly influences the lives of farmers.
Income Stability and Risk Mitigation
Policy-backed safety nets provide farmers with financial security during unforeseen challenges like crop failure or market fluctuations.
Access to Resources and Training
Well-designed policies ensure access to credit, education, and training, empowering farmers to adopt modern practices.
Impact on Consumers
Agricultural policy resonates with consumers' concerns.
Food Safety and Quality Assurance
Stringent regulations guarantee the safety and quality of food products, safeguarding public health.
Affordability and Accessibility
Effective policies prevent price gouging and ensure that nutritious food remains accessible to all segments of society.
Global Perspective on Agricultural Policy
Agricultural policy varies globally based on unique socio-economic and environmental contexts.
Diverse Approaches in Different Countries
Countries tailor policies to suit their specific needs, leading to a rich tapestry of agricultural strategies worldwide.
International Collaborations and Agreements
Cross-border partnerships facilitate knowledge exchange and harmonization of best practices.
The Future Of Agricultural Policy
Climate Change Adaptation
Policies must integrate strategies to mitigate and adapt to the impacts of climate change on agriculture.
Digitalization and Precision Agriculture
The future lies in harnessing digital tools and data analytics to optimize resource use and increase productivity.